Overview
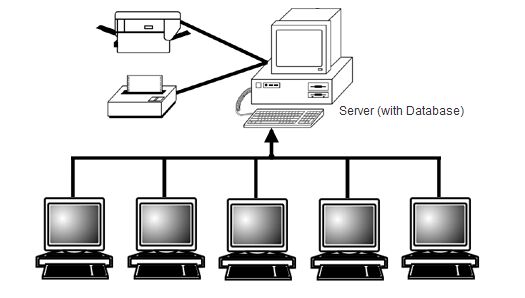
On a client/server network, every computer has a distinct role, that of either a client or a server. A server is designed to share its resources with the client computers on the network. Typically, servers are located in a secured area, such as locked office or back room, because they rarely accessed by users and run on a continuous basis. All the rest of the computers on the network function as clients
A dedicated server computer typically has a faster processor, more memory, and more storage space than a client because it might have to service dozens or even hundreds of users at the same time. High-performance servers also might use two or more processors, use the 64-bit version of the PCI expansion slot for server-optimized network interface cards, and have redundant power supplies.
Advantages
| • | Centralized - Resources and data security are controlled through the server. |
| • | Network access speeds are usually faster than those found on peer-to-peer networks, especially as the numbers of computers increase in the network. |
| • | Interoperability - All components (client/network/server) work together. |
| • | Flexibility - New technology can be easily integrated into system. |
| • | It’s more secure because if a client wants to communicate with another client he/she has to message to he/she and then it will first sent to the file server, where it is then routed to its destination. |
| • | Scalability - Any or all elements can be replaced individually as needs increase. |
| • | Accessibility - Server can be accessed remotely and across multiple platforms. |
Disadvantages
| • | Can cause network congestion when adding more users |
| • | Higher than anticipated costs are common occurrences |
| • | Maintenance - Large networks will require dedicated staff to ensure efficient operation |
| • | Dependence - When server goes down, operations will cease across the network |
| • | Lack of scalability - network operating systems (e.g... Novell Netware, Windows NT Server) are not very scalable. |
Installation
Client
A client computer communicates only with servers, not with other clients. A client system is a standard PC that is running an operating system such as Windows 9x, Windows Me, Windows 2000 Professional, or Windows XP. These versions of Windows contain the client software that enables the client computers to access the resources that servers share.
Server
The server runs a special network operating system—such as Windows NT Server, Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003, Linux, Unix, or Novell NetWare—that is designed solely to facilitate the sharing of its resources.